Learning the fundamental and important concepts of classification and focusing on solving spam detection using a naïve Bayes theorem.
The naïve Bayes classifier belong to family of probabilistic classifiers that computes the probabilities of each predictive feature of the data.
Below makes it special as its name indicates:
- Bayes: It maps the probabilities of observing input features given, belonging to class to probability distribution of class.
- Naïve: It assume that predictive features are mutually independent.
Bayes Theorem:

Example: If dangerous fires are rare (1%), but smoke is common (10%) due to barbecues, and 80% of dangerous fires make smoke then:

So, the “Probability of dangerous Fire when there is Smoke” is 8%.
Now to understand how naïve Bayes algorithm work in machine learning.
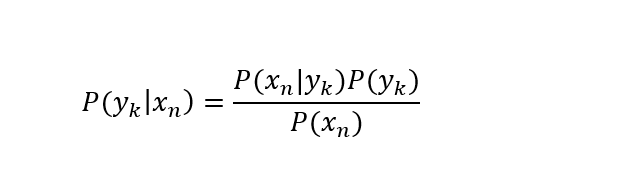


Now apply naïve Bayes classifier through an example “Spam email detection” with code implementation in Python.
Given some pseudo email as below and keep the Ham/Spam class information in the label variable where 1 represents Spam email and 0 for Ham mails. Spam email:

Non-Spam (Ham) email:

The next step is to clean the raw text data if it is required. In our example it is not require. Now extracting the features which are the term frequencies from the email text data.

Here the max_features parameter set to 100 means it will consider 100 most frequent terms. We can change the parameter to achieve better accuracy. This vectorizer change the email matrix (rows of word) to term matrix where each row is a term frequency vector for an email.

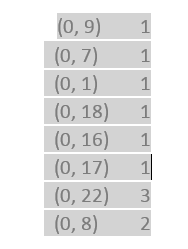
This vector is in the form of (row index, feature/term index) value (term frequency).
We can now build and train our naïve Bayes model. Starting with prior, first group the data based on label:

Here we set the smoothing parameter to 1. It can be either 0 or any positive value to achieve high performance.
likelihood is the conditional probability as mention in above.
Likelihood look like: {0: array([0.01851852, 0.01851852, 0.05555556, 0.01851852, 0.03703704,….])}
Now prior and likelihood ready, we can compute the posterior for the testing/new samples data.
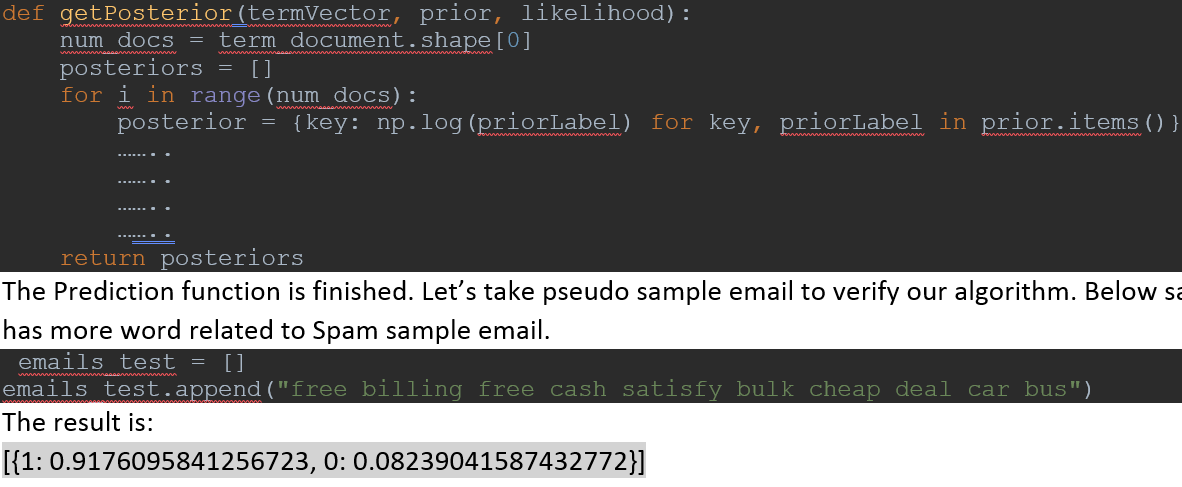
Now the result shows this testing sample is spam email because probability for spam is near about 91% and ham is less than 10%.
Let’s take another pseudo sample email to verify our algorithm. Below sample has more word related to Ham sample email.
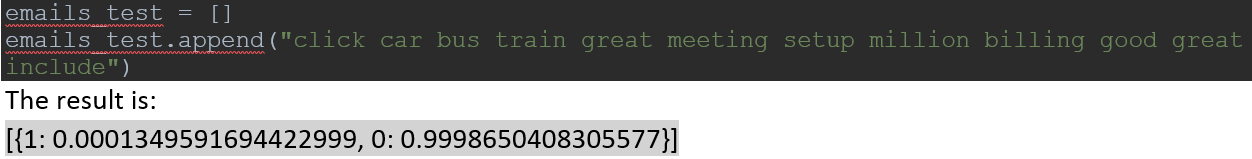
Now the result shows this testing sample is Ham email because probability for ham is near about 100% and spam is less than 1%.
Next step is to try with different combination of word for both Spam and Ham sample email and test the results.
After hand calculating spam email detection, we can take some genuine email data set taken from Enron email data set.
Furthermore, to evaluate our classifier performance we can randomly split the data set into training and testing set.
We can also use Area Under the Curve (AUC) of the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) to judge this model. I will cover this in next blog.
Manish Agrawal – Machine Learning Engineer.